In our rapidly evolving world, decision-making has never been more critical. Each choice, whether made by individuals, corporations, or governments, has the potential to shape our society in profound ways. In this context, understanding the social impact of decisions is not just important—it’s essential.
The concept of social impact refers to the effect of an action (or inaction) on the well-being and functioning of a community or society. This encompasses a broad range of outcomes, from economic and environmental to cultural and political. In today’s socio-political climate, where actions and decisions are intensely scrutinized and their repercussions widely felt, the consideration of social impact is vital.
Decisions can no longer be viewed in isolation. They are interconnected, influencing and being influenced by a complex web of societal factors. The rise of social media and digital communication has amplified the reach and consequences of decisions, making their social impact more immediate and visible. This interconnectedness means that decisions taken today can have lasting effects, shaping future generations and the world they will inhabit.
Therefore, understanding the social impact is not just about analyzing immediate outcomes but also about foreseeing long-term consequences. It’s about recognizing the responsibility that comes with decision-making power and striving to create positive change for a better future.
Table of Contents
Individual Decisions and Their Ripple Effects
The choices we make as individuals, though seemingly small, can have far-reaching effects on society. This is particularly evident in areas such as consumption habits, voting, and social media use. Each of these domains offers a clear illustration of how personal decisions can ripple out to influence the larger social fabric.
Consumption Habits: Our choices about what to buy, where to buy from, and how often to buy are not merely economic decisions; they are also social ones. When we choose products that are sustainably sourced, or opt for brands with ethical labor practices, we contribute to a demand for responsible business practices. This, in turn, can drive changes in how companies operate, affecting everything from environmental sustainability to workers’ rights. On the flip side, indiscriminate consumption can lead to negative outcomes like environmental degradation and exploitation of labor.
Voting: The act of voting is a direct and powerful way individuals influence society. Through voting, we help shape the policies and leaders that will govern our communities and nations. Our collective choices in the voting booth can lead to significant changes in areas like healthcare, education, and civil rights, thereby directly impacting the lives of millions.
Social Media Use: In the digital age, how we use social media is another potent form of individual decision-making. The content we share, the posts we like, and the narratives we endorse can collectively influence public opinion and societal norms. Social media platforms have become battlegrounds for ideological conflicts, with the potential to both unite and divide communities.
Ethical Consumerism: Ethical consumerism is a response to these ripple effects, where consumers use their purchasing power to effect positive social change. It involves choosing products and services that are ethically produced, with consideration for environmental sustainability, human rights, and social justice. The social implications of ethical consumerism are profound. It encourages businesses to adopt more responsible practices, promotes social awareness among consumers, and can even lead to legislative changes. By making informed choices, ethical consumers can drive a shift towards a more equitable and sustainable world.
The decisions we make every day, whether they’re about what to buy, how we vote, or how we interact on social media, are not just personal choices. They are powerful tools that shape the society we live in. Understanding this interconnectedness is crucial in harnessing our individual power to create positive social change.
Government Policies and Social Outcomes
Government decisions and policies play a pivotal role in shaping societies at both national and global levels. Their impact is often widespread, affecting various segments of society in diverse ways. To understand this impact, it is crucial to consider factors such as equity, justice, and sustainability.
National Scale:
Economic Policies: Recent government decisions in areas like taxation, minimum wage, and stimulus packages significantly affect the economy. These policies can either bridge or widen the wealth gap. For instance, progressive taxation and increased minimum wage can lead to greater income equality, while regressive taxation might exacerbate income disparities.
Healthcare Policies: Government decisions related to healthcare, especially in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, have had far-reaching implications. Policies on healthcare funding, vaccine distribution, and public health measures can greatly influence the well-being of citizens, often highlighting disparities in access to healthcare.
Environmental Policies: Decisions on environmental regulation, renewable energy investment, and climate change mitigation are critical. These policies not only address sustainability concerns but also impact economic and social sectors, such as job creation in green industries or the health effects of pollution.
Global Scale:
Climate Change Agreements: International policies on climate change, like the Paris Agreement, have profound global implications. These policies require nations to take collective action, impacting industries, economies, and communities worldwide, particularly in terms of mitigating the effects of climate change on vulnerable populations.
Trade Agreements: Global trade policies and agreements can have significant economic impacts, influencing job markets, industry growth, and consumer prices. They can either promote equitable growth across nations or result in exploitation and unfair practices.
Human Rights Policies: Decisions regarding international human rights, such as conventions on child labor, gender equality, and refugee treatment, are crucial. These policies reflect the global commitment to justice and equity and have a direct impact on the lives of marginalized groups.
Impact on Different Segments of Society:
The impact
of these policies is often felt differently across various segments of society. For example, economic policies might benefit certain industries or socioeconomic classes more than others. Similarly, environmental policies might have a more immediate impact on communities living in vulnerable areas, such as coastal regions or pollution-heavy zones.
Equity: Policies need to be assessed for their equitable impact. Do they provide equal opportunities and benefits for all, or do they favor certain groups over others? For instance, healthcare policies might improve access for some, but if they fail to address the needs of marginalized communities, they can perpetuate existing inequalities.
Justice: This involves evaluating whether policies uphold the principles of fairness and rights for all citizens. For instance, criminal justice reforms, immigration policies, and voting rights legislation are areas where government decisions can significantly affect social justice.
Sustainability: Assessing the sustainability of government policies involves looking at their long-term environmental, social, and economic impacts. Are these policies creating a foundation for a sustainable future, or are they contributing to further degradation of resources and inequalities?
Analyzing government policies from the perspective of their social outcomes requires a multifaceted approach. It’s essential to consider not only the immediate effects of these policies but also their long-term implications on equity, justice, and sustainability. This analysis helps in understanding how government decisions shape the fabric of society and the lives of its individuals.
Corporate Responsibility and Social Change
Corporations, as influential entities in the global economy, hold significant power in shaping societal norms and practices. Their decisions can have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of society, especially concerning environmental sustainability, labor practices, and ethical business conduct. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the role corporations can play in driving social change, leading to the rise of social entrepreneurship.
Impact of Corporate Decisions:
Environmental Sustainability: Corporate decisions greatly impact the environment. Choices regarding manufacturing processes, resource utilization, waste management, and carbon footprint have direct consequences on environmental health. Corporations adopting sustainable practices can lead to significant positive changes, such as reduced pollution, conservation of natural resources, and a slower rate of climate change. Conversely, neglecting environmental sustainability can exacerbate environmental crises.
Labor Practices: Corporations also have a profound impact on labor practices. This encompasses fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers’ rights. Ethical labor practices ensure a better quality of life for employees and can set industry standards. Poor labor practices, on the other hand, can lead to exploitation, unsafe work environments, and social unrest.
Ethical Business Conduct: The ethicality of corporate decisions, including transparency, accountability, and fairness, affects society’s trust in businesses. Unethical practices, such as corruption, tax evasion, and misleading advertisements, can erode public trust and harm the social fabric. Ethical conduct, conversely, can build consumer trust and loyalty, enhancing the company’s reputation and long-term success.
Role in Driving Social Change:
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Many corporations have embraced CSR, which involves taking proactive steps to contribute positively to society. This might include philanthropy, investing in community projects, or implementing environmentally friendly practices. CSR can lead to substantial improvements in societal well-being and environmental health.
Social Entrepreneurship: The rise of social entrepreneurship marks a significant shift in corporate philosophy. Social entrepreneurs focus on solving social problems through innovative business models. These businesses are not solely profit-driven but aim to achieve social objectives such as reducing poverty, improving education, or tackling environmental issues.
Influence on Policies and Norms: Corporations can influence social change by advocating for policies that support sustainable and ethical practices. Through lobbying efforts and partnerships with governments and NGOs, they can help shape policies that promote social welfare.
Setting Industry Standards: Corporations, especially industry leaders, have the power to set standards that others in the industry follow. By adopting responsible practices, they can encourage other companies to do the same, leading to industry-wide changes.
Corporations have a significant impact on society through their decisions and practices. Their role in environmental sustainability, ethical labor practices, and overall ethical business conduct is crucial. As drivers of social change, corporations, through CSR and social entrepreneurship, have the potential to address and solve critical social and environmental challenges. This evolving role of corporations reflects a broader shift in how business success is defined, with an increasing emphasis on social impact alongside financial performance.
Technological Advancements and Social Dynamics
Recent technological advancements, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence (AI), social media, and biotechnology, have significantly reshaped social interactions and structures. While these advancements offer numerous benefits, they also present several challenges and concerns.
AI and Social Dynamics:
Positive Implications: AI has revolutionized various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and education, by increasing efficiency and creating new opportunities for innovation. For instance, AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine are transforming healthcare delivery.
Negative Implications: AI also raises concerns, particularly around job displacement due to automation, and ethical issues such as bias in AI algorithms. These challenges can lead to social disparities and trust issues in technology.
Social Media’s Impact:
Enhanced Connectivity: Social media platforms have enabled unprecedented levels of connectivity, allowing people to maintain relationships over long distances and form new connections across global networks.
Echo Chambers and Polarization: However, social media can also contribute to the formation of echo chambers, where users are exposed only to information that reinforces their existing beliefs. This can lead to increased polarization and social division.
Mobilization of Social Movements: Social media has been crucial in organizing and spreading awareness about social movements. It has given a voice to marginalized groups and played a key role in movements like the Arab Spring and Black Lives Matter.
Biotechnology and Society:
Medical Advancements: Biotechnology has led to significant medical breakthroughs, including gene therapy and CRISPR technology, which have the potential to cure genetic diseases and improve quality of life.
Ethical and Social Concerns: These advancements also pose ethical questions, such as the implications of genetic editing and cloning. There are concerns about the accessibility of these technologies, potentially widening the gap between different socio-economic groups.
Cross-Cutting Concerns:
Privacy Concerns: Advancements in technology have raised significant privacy concerns. Data breaches, surveillance, and misuse of personal data are growing issues that affect trust and security in the digital space.
Digital Divide: The disparity in access to technology, known as the digital divide, exacerbates social inequalities. People without access to the internet and modern technology are increasingly disadvantaged in education, healthcare, and employment.
Dependence on Technology: There is an increasing reliance on technology in daily life, which raises concerns about the loss of certain skills and the potential consequences of technology failures or cyber-attacks.
While technological advancements offer immense potential for positive change and innovation, they also present significant challenges. These include concerns about privacy, the digital divide, ethical dilemmas, and the potential for increased social division. Balancing these factors is crucial in ensuring that technological progress contributes positively to social dynamics and does not exacerbate existing disparities.
The Role of Education and Awareness
Education systems and public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes and influencing social outcomes. They are powerful tools for fostering knowledge, shaping attitudes, and driving behavioral changes that can lead to positive social transformation.
Influence of Education Systems:
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: Education systems that emphasize critical thinking skills empower individuals to make informed decisions. By teaching students to analyze information, question assumptions, and consider diverse perspectives, education fosters more thoughtful and responsible decision-making.
Social Responsibility: Education can instill a sense of social responsibility. By integrating topics like civic education, environmental stewardship, and social justice into curricula, schools can encourage students to engage in societal issues and contribute to positive change.
Equity and Inclusion: Educational institutions that prioritize equity and inclusion can help break down barriers of discrimination and inequality. By providing equal opportunities for all students and addressing diverse needs, education systems can play a significant role in creating more equitable societies.
Impact of Public Awareness Campaigns:
Changing Attitudes and Behaviors: Effective public awareness campaigns can significantly change societal attitudes and behaviors. Campaigns that highlight issues like public health, environmental protection, and human rights can mobilize public opinion and inspire collective action.
Spreading Information: In the age of misinformation, public awareness campaigns can disseminate accurate and reliable information, helping people make informed choices about critical issues like health, safety, and civic responsibilities.
Successful Examples of Education and Awareness Leading to Social Change:
Environmental Education: The incorporation of environmental education in schools has led to a generation more aware and concerned about issues like climate change, conservation, and sustainability. This awareness has translated into increased environmental activism and more environmentally friendly behaviors in society.
Public Health Campaigns: Campaigns like anti-smoking, safe driving, and HIV/AIDS awareness have successfully changed public behaviors and attitudes, leading to improved health outcomes. For example, anti-smoking campaigns have significantly reduced smoking rates and associated health problems.
Human Rights Education: Educational initiatives that focus on human rights, gender equality, and diversity have fostered greater tolerance and acceptance in society. They have played a crucial role in advancing rights for marginalized groups and promoting social justice.
Financial Literacy Programs: Education programs aimed at improving financial literacy have empowered individuals to make better financial decisions, contributing to economic stability and growth.
Education systems and public awareness campaigns are vital in shaping a society’s decision-making and social outcomes. By fostering knowledge, critical thinking, and awareness of societal issues, they can lead to significant positive changes, from improved public health and environmental conservation to the promotion of human rights and social justice.
Case Studies on Social Impact
To illustrate the concept of social impact, let’s explore a few case studies from different domains. These examples highlight how specific initiatives or events have led to significant social changes, reflecting the diverse ways social impact can manifest.
- The Microfinance Revolution: Grameen Bank in Bangladesh
Background: Founded by Muhammad Yunus in 1980, Grameen Bank pioneered the concept of microfinance – providing small loans to the impoverished without requiring collateral.
Social Impact: Grameen Bank’s model empowered millions of poor, especially women, by providing them with the financial means to start small businesses. This led to improved family incomes, better education for children, and increased empowerment for women, fundamentally altering the socio-economic landscape of rural Bangladesh.
- The Green Revolution in Agriculture
Background: In the mid-20th century, the Green Revolution introduced high-yield crop varieties and modern agricultural techniques to developing countries.
Social Impact: This revolution significantly increased food production, reducing famine and hunger in many parts of the world, particularly in Asia and Latin America. However, it also had environmental impacts, such as increased use of chemical fertilizers and water, and socio-economic implications, including the marginalization of small farmers.
- The Anti-Apartheid Movement in South Africa
Background: The anti-apartheid movement was a global effort to end racial segregation and discrimination in South Africa, characterized by widespread protests, boycotts, and civil disobedience.
Social Impact: This movement led to the dismantling of apartheid laws and the establishment of a democratic government in South Africa. It also served as a powerful example of the effectiveness of international solidarity and nonviolent resistance in combating social injustices.
- The Impact of Social Media on the Arab Spring
Background: The Arab Spring, a series of anti-government protests and uprisings, erupted across the Arab world in 2010 and 2011. Social media played a crucial role in organizing, communicating, and spreading information about the protests.
Social Impact: The use of social media during the Arab Spring demonstrated its power in mobilizing for political and social change. It led to the overthrow of several governments and sparked a global conversation about democracy, freedom, and the role of social media in social movements.
- COVID-19 Pandemic and Remote Work Revolution
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 forced a rapid shift to remote work for many businesses and industries worldwide.
Social Impact: This shift has had a profound impact on work-life balance, urban planning, and the digital divide. It accelerated technological adoption and could have long-term effects on how work is structured, potentially leading to greater flexibility but also highlighting disparities in access to technology.
These case studies demonstrate the breadth and depth of social impact across various fields. They show how financial initiatives, agricultural changes, political movements, technological advancements, and global crises can lead to profound and lasting social changes, both positive and negative.
Quotes on Social Impact
Here are some insightful quotes on social impact, each reflecting different perspectives and insights on the importance and influence of social actions and initiatives:
Margaret Mead: “Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world; indeed, it’s the only thing that ever has.”
This quote emphasizes the power of collective action, no matter how small the group, in driving significant social change.
Nelson Mandela: “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.”
Mandela highlights the transformative power of education in shaping society and influencing global change.
Mahatma Gandhi: “Be the change that you wish to see in the world.”
Gandhi’s words inspire individual responsibility and action in contributing to social change.
Martin Luther King Jr.: “Life’s most persistent and urgent question is, ‘What are you doing for others?'”
This quote encourages self-reflection on one’s contribution to the welfare of others, underlining the importance of service and altruism in social impact.
Mother Teresa: “I alone cannot change the world, but I can cast a stone across the waters to create many ripples.”
Mother Teresa’s words illustrate the concept that individual actions, while seemingly small, can initiate widespread impact.
Barack Obama: “Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other time. We are the ones we’ve been waiting for. We are the change that we seek.”
Obama’s statement emphasizes the importance of taking initiative and recognizing one’s own power in creating social change.
Jane Goodall: “What you do makes a difference, and you have to decide what kind of difference you want to make.”
Goodall’s quote is a call to conscious action, reminding us that our decisions and actions have impacts, and it’s up to us to choose their direction and nature.
Bill Drayton: “Social entrepreneurs are not content just to give a fish or teach how to fish. They will not rest until they have revolutionized the fishing industry.”
This quote captures the essence of social entrepreneurship, which is about creating far-reaching and systemic changes in society.
These quotes collectively underscore the diverse aspects of social impact, from individual responsibility to the power of education, and the transformative potential of collective action and innovative thinking.
Interviews on Social Impact
Conducting interviews on social impact can provide valuable insights into how individuals, organizations, and communities perceive and contribute to societal change. Here are some ideas and questions that could be used to guide interviews on this topic:
Interview Ideas:
Social Entrepreneurs:
Focus: Their journey, motivations, challenges, and the impact of their work.
Example Interviewee: Founder of a company with a strong social mission.
Community Leaders:
Focus: Grassroots initiatives, community challenges, and effective strategies for local change.
Example Interviewee: Leader of a community organization or local activist.
Policy Makers:
Focus: The role of policy in shaping social outcomes and the process of creating impactful legislation.
Example Interviewee: Local or national government official.
Educators:
Focus: The role of education in societal change and how educational institutions can be catalysts for social impact.
Example Interviewee: Teacher, professor, or education reform advocate.
Corporate Executives with CSR Initiatives:
Focus: Corporate social responsibility, ethical business practices, and integrating social goals into business models.
Example Interviewee: CSR manager or executive in a socially responsible corporation.
Researchers in Social Sciences:
Focus: Academic perspectives on social change, evidence-based insights, and the role of research in informing policy and practice.
Example Interviewee: Academic or researcher specializing in social issues.
Sample Interview Questions:
What inspired you to become involved in [specific area of social impact]?
Aims to understand personal motivation and background.
Can you describe a specific project or initiative you have worked on that had a significant social impact?
Seeks detailed insights into practical applications and outcomes.
What are the biggest challenges you face in your efforts to create social change?
Explores obstacles and how they are navigated.
How do you measure the impact of your work, and what are some of the most notable outcomes you’ve observed?
Focuses on assessment, results, and reflections on effectiveness.
In your opinion, what are the key elements for successful social impact?
Seeks expert perspective on what constitutes successful strategies.
How do you see the future of social impact in your field? What changes or developments do you anticipate?
Discusses future trends and personal outlook.
What advice would you give to someone looking to make a positive social impact in their community or field?
Asks for guidance and suggestions for aspiring changemakers.
These interviews can offer rich, diverse, and nuanced perspectives on social impact, providing an in-depth understanding of various approaches and the challenges and successes encountered in different sectors.
Expert Opinion on Social Impact
Expert opinions on social impact often come from individuals with extensive experience or academic background in fields like social sciences, public policy, environmental studies, or business ethics. They provide valuable insights into the complexities and nuances of creating and measuring social impact. Here are some synthesized expert perspectives on the topic:
On Measuring Social Impact:
Experts often emphasize that measuring social impact is challenging but essential. They might advocate for a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to capture the full scope of an initiative’s effects. Metrics can include direct outcomes (like the number of people positively affected) and indirect outcomes (like changes in community well-being).
The Role of Collaboration:
Many emphasize the importance of collaboration across sectors. Partnerships between NGOs, governments, businesses, and communities are seen as vital for addressing complex social issues. Experts often note that collaborative efforts can lead to more sustainable and scalable impact.
Sustainability and Long-Term Impact:
Sustainability is a key focus. Experts argue that for social impact to be meaningful, it must be sustainable over the long term, addressing the root causes of issues rather than just symptoms. This often involves systemic change, which is more challenging but more transformative.
Ethical Considerations:
Ethical considerations are highlighted, particularly in the context of respecting and understanding the needs and values of the communities involved. This includes avoiding paternalistic approaches and ensuring that initiatives are culturally sensitive and community-driven.
Technology’s Role:
The increasing role of technology in amplifying social impact is frequently discussed. Experts point to how digital tools can enhance reach and efficiency but also caution about issues like the digital divide and ethical concerns around data privacy.
Impact of Social Entrepreneurship:
Social entrepreneurship is often praised for its innovative approach to solving social problems. Experts note that these ventures can challenge traditional business models and offer new ways to address social issues effectively and sustainably.
Global Trends and Local Contexts:
There’s a recognition of the need to balance global trends with local contexts. While global issues like climate change require widespread action, solutions must be adapted to fit local cultures and environments.
Education’s Role:
The transformative power of education is a common theme. Experts believe that educating current and future generations about social issues is crucial for long-term societal change.
Government Policies and Systemic Change:
The impact of government policies on societal structures and the importance of advocating for policy change is often emphasized. Experts argue that while individual and corporate actions are important, systemic change often requires policy interventions.
Challenges of Funding and Resource Allocation:
The challenge of securing sustainable funding for social impact initiatives is frequently noted. Experts stress the importance of innovative funding models and the responsible allocation of resources to maximize impact.
Expert opinions on social impact underscore the complexity of effecting and measuring change, the importance of ethical and sustainable approaches, the potential of technology and innovation, and the need for collaboration across sectors and disciplines.
Issues of Social Impact
Issues of social impact are diverse and multifaceted, reflecting the complexity of societal challenges and the varied effects of actions taken by individuals, organizations, and governments. Here are some key issues in the realm of social impact:
Environmental Sustainability:
Challenges include climate change, pollution, loss of biodiversity, and unsustainable resource use. The social impact of these issues is vast, affecting health, livelihoods, and global ecosystems.
Economic Inequality:
Issues like poverty, income disparity, and unequal access to opportunities create significant social impacts. Addressing these requires initiatives focused on economic inclusion, fair trade, and equitable growth.
Healthcare and Public Health:
Access to affordable and quality healthcare is a major issue. Public health challenges, such as pandemics and chronic diseases, have wide-ranging impacts on societies.
Education and Access to Knowledge:
Inequalities in education and the digital divide impact social mobility and economic opportunities. Quality education is crucial for empowering individuals and fostering innovation.
Human Rights and Social Justice:
Issues around gender equality, racial justice, and the rights of marginalized groups remain central to social impact discussions. Advocacy and legal reforms are key in addressing these challenges.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
The role of businesses in society, ethical business practices, and the integration of social goals into business models are ongoing issues. CSR and ethical consumerism are responses to these challenges.
Technological Advancements and Ethics:
The impact of technology on privacy, employment, and social interactions presents new challenges. Ethical considerations in AI, data security, and the digital divide are critical issues.
Community Development and Participation:
Ensuring community involvement in development projects and decision-making processes is vital. This includes addressing issues of urban development, rural support, and community resilience.
Globalization and Cultural Preservation:
Balancing the benefits of globalization with the need to preserve cultural identities and traditions is a complex issue. It involves navigating economic integration with respect for local customs and heritage.
Disaster Response and Humanitarian Aid:
Challenges in effectively responding to natural disasters and humanitarian crises, including issues of coordination, sustainability, and addressing the needs of the most
vulnerable populations, are significant. Ensuring that aid is effective, timely, and culturally sensitive is crucial.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
Meeting the United Nations’ SDGs presents a comprehensive set of challenges, encompassing environmental, social, and economic aspects. Achieving these goals requires coordinated global efforts.
Mental Health and Wellbeing:
The growing recognition of mental health as a critical component of overall health highlights the need for accessible mental health services and the removal of stigma associated with mental illness.
Youth Engagement and Empowerment:
Engaging and empowering the younger generation in social issues is key for long-term societal change. This involves addressing youth unemployment, education reform, and civic participation.
Migration and Refugee Crises:
Issues surrounding migration, including the treatment of refugees and immigrants, integration policies, and the causes of forced migration, such as conflict and climate change, are increasingly important.
Ethical Supply Chains:
Ensuring transparency and ethical practices in global supply chains, particularly in industries like clothing and electronics, is a pressing issue. This includes addressing labor rights and environmental impacts.
These issues highlight the scope and complexity of social impact. Addressing them requires multi-faceted approaches, collaborative efforts, and innovative solutions that consider both immediate needs and long-term sustainability.
Global Perspective on Social Impact
The concept of social impact from a global perspective encompasses a wide range of initiatives and effects that span across borders, cultures, and economies. It reflects the interconnectedness of our world, where actions taken in one part of the globe can have significant repercussions in another. Here are some key aspects of social impact from a global viewpoint:
Cross-Border Challenges and Solutions:
Many social issues, such as climate change, public health crises (like the COVID-19 pandemic), and economic disparities, are global in nature. Addressing these challenges often requires international cooperation and solutions that transcend national boundaries.
Cultural Sensitivity and Diversity:
Understanding and respecting cultural differences is crucial in global social impact initiatives. Solutions effective in one cultural context may not be suitable in another. Emphasizing cultural sensitivity ensures that interventions are relevant, respectful, and effective.
Technology’s Global Reach:
Advances in technology, particularly the internet and mobile communications, have created new pathways for social impact. They have enabled global connectivity, allowing ideas and solutions to be shared rapidly across the world. However, this also raises issues like the digital divide, where some regions have less access to technology.
Global Economic Integration:
The global economy is deeply interconnected, meaning that economic policies and corporate practices in one country can have far-reaching effects on others. For example, trade agreements or multinational corporations’ operations can impact global labor practices, environmental standards, and economic development.
International Development and Aid:
Development projects and humanitarian aid from various international organizations and NGOs play a significant role in global social impact. These initiatives often focus on poverty reduction, education, healthcare, and disaster relief in less developed countries.
Migration and Global Mobility:
Issues surrounding migration, including refugees and economic migrants, are significant aspects of global social impact. Policies and attitudes towards migrants can have profound implications for human rights and social integration.
Global Governance and Policy Making:
International bodies and agreements, such as the United Nations, the World Health Organization, and the Paris Agreement on climate change, illustrate the role of global governance in addressing worldwide social issues.
Social Movements and Global Solidarity:
Social movements, often fueled by social media and digital communication, can quickly become global. Movements like #MeToo, Black Lives Matter, and climate change activism have shown how solidarity and activism can cross national borders, leading to global discussions and actions.
Sustainability and Future Generations:
There is a growing recognition of the need to make decisions that not only address current issues but also consider their long-term impact on future generations, emphasizing sustainability and the responsible use of resources.
A global perspective on social impact recognizes the interconnected nature of our world and the need for collaborative, culturally sensitive, and sustainable approaches to address the complex challenges we face. It involves thinking beyond local and national boundaries to embrace a more holistic, global view of societal progress and well-being.
Examples of Social Impact
Social impact can be observed in various forms and through a multitude of initiatives across different sectors. Here are some notable examples:
Microfinance Institutions:
Example: Grameen Bank in Bangladesh.
Impact: Revolutionized access to financial services for the poor, particularly women, enabling them to start small businesses and improve their livelihoods.
Environmental Conservation Efforts:
Example: The reforestation projects in the Amazon Rainforest.
Impact: Contributed to the preservation of biodiversity, the mitigation of climate change effects, and the protection of indigenous communities’ livelihoods.
Public Health Campaigns:
Example: The global polio eradication initiative.
Impact: Dramatically reduced the incidence of polio worldwide, moving closer to complete eradication of the disease.
Educational Initiatives:
Example: Khan Academy’s online learning platform.
Impact: Provided free, high-quality educational resources globally, democratizing access to education, particularly in underserved communities.
Social Entrepreneurship:
Example: TOMS Shoes’ “One for One” model.
Impact: Pioneered a business model that combined profit with social good, providing shoes (and later, eyewear and water) to those in need for each product sold.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Programs:
Example: Google’s renewable energy initiatives.
Impact: Invested in sustainable energy sources, significantly contributing to the reduction of carbon footprint in the tech industry.
Community Development Projects:
Example: The Harlem Children’s Zone in New York City.
Impact: Improved outcomes in education, health, and employment for children and families in Harlem through comprehensive, community-focused programs.
Advocacy and Legal Reform:
Example: The Marriage Equality movement.
Impact: Led to significant legal and social changes, culminating in the legalization of same-sex marriage in many countries, promoting LGBTQ+ rights.
Technological Innovations for Social Good:
Example: Mobile apps for mental health support.
Impact: Increased access to mental health resources, providing support and reducing stigma around mental health issues.
Disaster Relief and Humanitarian Aid:
Example: International response to the Haiti earthquake in 2010.
Impact: Provided critical aid and support for rebuilding efforts in the wake of a devastating natural disaster.
These examples reflect the diverse ways in which social impact can be achieved, spanning areas from poverty alleviation and environmental protection to education, health, and human rights. They demonstrate how targeted actions, whether through business models, technology, community programs, or advocacy, can lead to significant and positive changes in society.
A Chart Table for Social Impact
Here’s a chart table summarizing various social impact initiatives across different sectors, along with their key impacts:
| # | Initiative | Sector | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grameen Bank | Microfinance | Financial inclusion for the poor |
| 2 | Amazon Reforestation | Environmental Conservation | Biodiversity preservation & climate action |
| 3 | Polio Eradication | Public Health | Near eradication of polio |
| 4 | Khan Academy | Education | Free, global access to quality education |
| 5 | TOMS Shoes | Social Entrepreneurship | Shoes & other essentials donated for each item sold |
| 6 | Google Renewable Energy | Corporate Social Responsibility | Investment in sustainable energy solutions |
| 7 | Harlem Children’s Zone | Community Development | Improved outcomes in education & health |
| 8 | Marriage Equality | Advocacy and Legal Reform | Legalization of same-sex marriage |
| 9 | Mental Health Apps | Technology and Health | Increased access to mental health resources |
| 10 | Haiti Earthquake Aid | Disaster Relief | Aid and support for disaster recovery |
This table provides a quick overview of how different initiatives have contributed to significant social changes in their respective areas.
An Infographic on Social Impact

Here is an infographic that visually represents various social impact initiatives across different sectors. It includes visual representations of the Grameen Bank, Amazon Reforestation, Polio Eradication, Khan Academy, TOMS Shoes, Google’s Renewable Energy initiative, Harlem Children’s Zone, Marriage Equality, Mental Health Apps, and Haiti Earthquake Aid. Each image symbolizes the key impacts of these initiatives in a colorful and engaging way.
A Graph for Social Impact
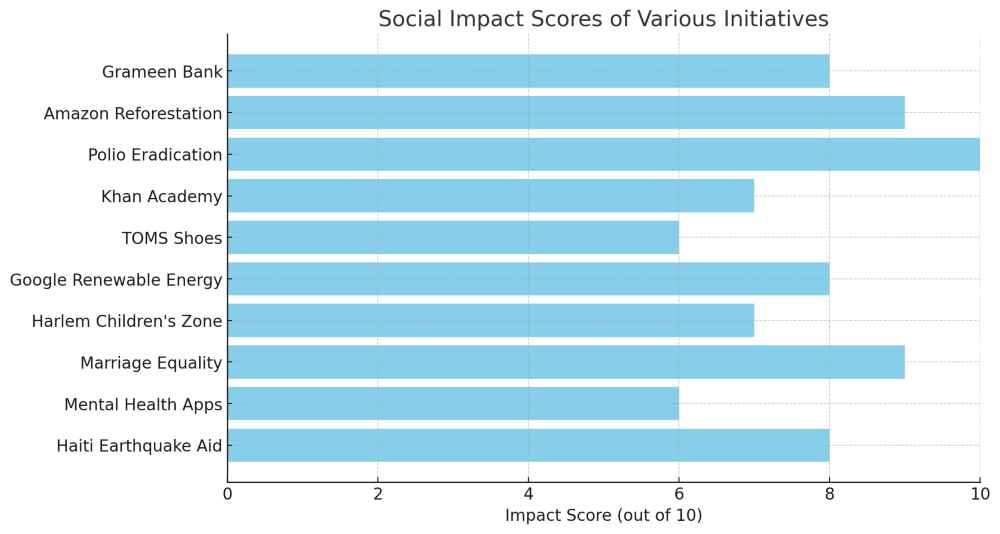
Here’s a graph displaying hypothetical social impact scores for various initiatives. Each initiative, such as the Grameen Bank, Amazon Reforestation, and others, is assigned a score out of 10, representing its impact. This visual representation provides a comparative view of their relative impacts in a clear and concise manner.
Conclusion
The exploration of social impact across various domains highlights the profound and diverse ways in which organizations, policies, technologies, and individuals can influence society. From microfinance initiatives like Grameen Bank to large-scale environmental efforts like Amazon Reforestation, each case presents unique contributions and challenges. The common thread among these examples is their ability to bring about significant, often transformative changes in communities, economies, and environments.
Key Points:
Multifaceted Nature of Social Impact: Social impact is not limited to a single domain; it encompasses a wide range of areas including finance, health, education, environment, technology, and civil rights.
Interconnectivity of Actions and Outcomes: Individual and collective actions in one area can have ripple effects across various sectors. For instance, corporate social responsibility initiatives not only affect business practices but also have broader social and environmental implications.
Challenges and Opportunities in Measuring Impact: Assessing the social impact is complex and requires both quantitative and qualitative approaches. While some impacts are easily quantifiable, others, like changes in social norms or community well-being, are more nuanced.
The Role of Collaboration: Effective social change often requires collaboration across different sectors. Partnerships between NGOs, governments, corporations, and communities are crucial for addressing complex social issues.
Ethical and Sustainable Approaches: There is a growing emphasis on the ethical and sustainable dimensions of social impact, focusing on long-term benefits and minimizing negative consequences.
Innovation and Adaptation: Innovations, particularly in technology and social entrepreneurship, are constantly reshaping the landscape of social impact, requiring continuous adaptation and learning.
Education and Awareness: These are pivotal in fostering a society that is aware of and engaged in social issues. They play a crucial role in shaping future generations and informing public opinion.
Global and Local Dimensions: Social impact must balance global trends and challenges with local contexts and needs, ensuring that global initiatives are adapted to fit local realities.
Understanding and contributing to social impact requires a comprehensive and nuanced approach. It involves considering the ethical, sustainable, and long-term implications of actions, and recognizing the interconnectedness of various social, economic, and environmental factors.
Analysis Report on Social Impact
Executive Summary:
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of social impact across various sectors and initiatives globally. It examines how different actions and strategies contribute to societal change, addressing the complexity and interconnectivity of global challenges. The report also highlights key trends, challenges, and opportunities in the field of social impact.
- Introduction:
Purpose: To understand and articulate the diverse aspects of social impact, examining how they contribute to global societal development.
Scope: The report covers multiple sectors including environmental sustainability, public health, education, economic development, and human rights.
- Global Challenges and Social Impact:
Climate Change: Examines the efforts to combat climate change through sustainable practices and policies.
Public Health: Focuses on global health challenges, including pandemics and healthcare accessibility.
Economic Disparities: Analyzes initiatives aimed at reducing poverty and promoting economic inclusion.
- Technological Advancements and Their Impact:
Digital Revolution: Explores the impact of the digital revolution on social dynamics, including the digital divide and data privacy concerns.
Innovation in Healthcare: Looks at technological advancements in healthcare and their implications for global health.
- Role of Education and Awareness:
Education Systems: Discusses the role of education in fostering social change and the importance of inclusive and equitable educational practices.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Analyzes the effectiveness of various campaigns in altering public perceptions and behaviors.
- Corporate Responsibility and Social Entrepreneurship:
CSR Initiatives: Evaluates the impact of CSR initiatives in various industries.
Social Entrepreneurship: Investigates how new business models are addressing social issues innovatively and sustainably.
- Government Policies and International Cooperation:
Policy Making: Assesses the role of government policies in shaping social outcomes.
International Agreements: Examines the effectiveness of international agreements and collaborations in addressing global challenges.
- Case Studies and Best Practices:
Success Stories: Presents case studies of successful social impact initiatives across different sectors.
Lessons Learned: Extracts key lessons and best practices from these case studies.
- Challenges and Barriers:
Implementation Gaps: Identifies common challenges in implementing social impact initiatives.
Resource Allocation: Discusses issues related to funding and resource management.
- Future Outlook and Recommendations:
Emerging Trends: Explores emerging trends in the field of social impact.
Strategic Recommendations: Provides strategic recommendations for organizations and policymakers to enhance social impact.
- Conclusion:
Summary of Findings: Concisely summarizes the key findings of the report.
Call to Action: Emphasizes the need for continued effort and collaboration in creating positive social impact.
Appendices:
Data Sources: Lists the data sources and methodologies used in the report.
Additional Resources: Provides additional resources for further reading and research.
This report aims to offer a nuanced understanding of social impact, providing insights and guidance for various stakeholders involved in creating and shaping social change.
Analytical Data Report on Social Impact
Executive Summary:
This report presents a global analysis of social impact, utilizing quantitative and qualitative data to assess the effectiveness and reach of various initiatives across different sectors. It aims to provide a data-driven understanding of how social impact efforts are contributing to global change, identifying trends, successes, and areas needing improvement.
- Introduction:
Objective: To offer an analytical perspective on the scale and scope of social impact globally, leveraging data to inform decision-making and strategy development.
Scope: The report encompasses a wide array of sectors, including environmental conservation, public health, economic empowerment, education, and technological innovation.
- Methodology:
Data Collection: Description of data sources, including international databases, surveys, case studies, and reports from NGOs, governments, and international organizations.
Analytical Approach: Outline of the statistical and analytical methods used to interpret the data.
- Sector-wise Global Impact Analysis:
Environmental Sustainability: Analysis of carbon footprint reduction, biodiversity conservation efforts, and sustainable resource use.
Public Health: Data on global health initiatives, vaccination rates, and healthcare access.
Economic Development: Statistics on poverty alleviation, microfinance, and job creation.
Educational Outreach: Data on literacy rates, educational access, and the impact of educational programs.
- Technological Advancements and Impact:
Digital Transformation: Examination of the digital divide, internet accessibility, and the impact of digital technologies on social change.
Healthcare Technologies: Data on the adoption of new medical technologies and their impact on global health outcomes.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Social Entrepreneurship:
CSR Initiatives: Analysis of the impact of CSR programs across various industries.
Social Enterprises: Data on the reach and effectiveness of social enterprises in addressing social issues.
- Impact of Government Policies and International Cooperation:
Policy Impact Analysis: Assessment of the effectiveness of various government policies in different countries on social outcomes.
International Agreements: Evaluation of the impact of international treaties and agreements.
- Challenges and Limitations:
Data Gaps: Identification of areas where data is lacking or insufficient.
Implementation Challenges: Analysis of common barriers to effective implementation of social impact initiatives.
- Trends and Future Outlook:
Emerging Trends: Insights into emerging trends in social impact, based on data analysis.
Predictive Analysis: Projections and predictions for future developments in social impact, based on current data trends.
- Conclusion and Recommendations:
Key Findings: Summary of the most significant findings from the data analysis.
Strategic Recommendations: Data-driven recommendations for organizations, governments, and other stakeholders.
- Appendices:
Appendix A: Detailed data tables and charts.
Appendix B: List of data sources and references.
Appendix C: Case studies and in-depth sector analyses.
This report provides a comprehensive and analytical view of the current state of social impact globally, offering valuable insights for policymakers, organizations, and other stakeholders committed to making a positive difference in the world.

References
Here are some references you might consider, along with suggestions on where you might find them:
United Nations Reports:
Description: Reports on various global issues such as poverty, education, and climate change.
Where to Find: Visit the official United Nations website and look for publications or reports in their respective sections (e.g., UNDP, UNESCO, UNEP).
World Bank Data:
Description: Comprehensive data on global economic and social indicators.
Where to Find: Access the World Bank’s official website and navigate to their ‘Data’ section.
World Health Organization (WHO) Publications:
Description: Reports and statistics on global health issues.
Where to Find: Visit the WHO’s official website and explore their ‘Publications’ section.
Pew Research Center:
Description: Surveys and studies on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends globally.
Where to Find: Go to the Pew Research Center’s website and search for relevant studies.
Global Environmental Data:
Description: Data on environmental indicators and sustainability.
Where to Find: Look for environmental data on websites of organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) Reports:
Description: Economic and social policy reports.
Where to Find: Visit the OECD’s official website and access their ‘Reports’ section.
Academic Journals:
Description: Peer-reviewed articles and research papers on social impact.
Where to Find: Use academic databases like JSTOR, Google Scholar, or university libraries.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Reports:
Description: Reports from major corporations on their CSR initiatives.
Where to Find: Check the official websites of major corporations under sections typically labeled ‘Sustainability’, ‘CSR’, or ‘Our Impact’.
Social Entrepreneurship Case Studies:
Description: Detailed case studies of social enterprises.
Where to Find: Look for publications from business schools or institutions like the Stanford Social Innovation Review.
Government Policy Documents:
Description: Official government documents outlining policies on social issues.
Where to Find: Access government websites, particularly departments or ministries focused on social issues, health, environment, education, etc.
For the most accurate and current information, it’s essential to visit these websites directly and
Search for the specific reports or data that you need. These organizations frequently update their resources and publications, offering a wealth of information for comprehensive research on social impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Social Impact
Here are some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about social impact, along with their answers:
- What is social impact?
Answer: Social impact refers to the effect an organization’s actions have on the well-being of the community and society at large. It encompasses a broad range of outcomes including environmental, economic, and social changes.
- How is social impact measured?
Answer: Social impact is measured using a variety of metrics, depending on the specific goals of the project or initiative. These can include quantitative measures like the number of people served or qualitative assessments like surveys and interviews to gauge changes in community well-being.
- Why is social impact important for businesses?
Answer: Social impact is important for businesses because it strengthens community relations, enhances brand reputation, and can lead to sustainable business practices. It also aligns business operations with societal needs and expectations, which is increasingly valued by consumers, employees, and investors.
- Can social impact initiatives be profitable?
Answer: Yes, social impact initiatives can be profitable. Many businesses integrate social impact into their core strategies, leading to innovative products and services that address social needs while generating revenue.
- What is the difference between social impact and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility)?
Answer: Social impact refers to the effects of any action on society, while CSR is a business model where companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and interactions with stakeholders.
- How do non-profits contribute to social impact?
Answer: Non-profits contribute to social impact by addressing various societal issues such as poverty, education, health care, and environmental conservation, often filling gaps not addressed by the private sector or government.
- What role does technology play in social impact?
Answer: Technology plays a significant role in social impact by providing innovative solutions to social problems, enhancing communication and outreach, improving efficiency in service delivery, and enabling data collection and analysis for better impact assessment.
- How can individuals contribute to social impact?
Answer: Individuals can contribute to social impact through volunteer work, donations, ethical consumerism, advocacy, and by being informed and engaged citizens.
- What are some challenges in creating social impact?
Answer: Challenges in creating social impact include limited resources and funding, difficulties in measuring and showing tangible results, balancing economic goals with social objectives, addressing diverse stakeholder needs, and ensuring sustainable and scalable impact.
- How do governments influence social impact?
Answer: Governments influence social impact through policy-making, funding and supporting social programs, regulating corporate social practices, and providing essential public services that address social issues like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- What is social entrepreneurship?
Answer: Social entrepreneurship is the practice of developing, funding, and implementing solutions to social, cultural, or environmental issues. It combines the innovation and resourcefulness of business entrepreneurship with a mission to positively impact society.
- Can social impact be negative?
Answer: Yes, social impact can be negative when actions or policies inadvertently harm communities or the environment, such as through environmental degradation, worsening inequality, or adverse cultural impacts.
- What is the role of public awareness in social impact?
Answer: Public awareness is crucial in social impact as it educates and mobilizes the community around important issues, influences public opinion and behavior, and can lead to increased support and participation in initiatives aimed at social change.
- Are there specific industries known for high social impact?
Answer: Industries such as renewable energy, education, healthcare, and sustainable consumer goods are often associated with high social impact due to their direct influence on societal well-being and environmental sustainability.
- How can impact investing contribute to social change?
Answer: Impact investing contributes to social change by directing capital to enterprises and initiatives that generate social or environmental benefits along with financial returns, thereby using market-based solutions to address societal challenges.
These FAQs provide a basic understanding of social impact, its importance, challenges, and the various ways it can be achieved and measured.









Leave a Reply