Business ethics encompasses the study of suitable policies and practices within the business world, focusing on potentially contentious issues. This includes corporate governance, insider trading, bribery, discrimination, and more. The primary goal is to ensure that businesses operate in a manner that is not only legal but also ethical, balancing profit-making with societal and environmental responsibilities. In This article, we describe The Essential Role of a Code of Ethics in Business Ethics.
Table of Contents
Importance of a Code of Ethics
A code of ethics in business ethics is vital in the realm of business ethics. It serves as a guiding document that outlines the ethical principles and standards that a business commits to following. This code plays a crucial role in maintaining trust and credibility with stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and the wider community. It helps in making informed decisions, especially in situations where legal and ethical boundaries may not be clear-cut. By adhering to a well-crafted code of ethics, businesses can avoid legal issues, enhance their reputation, and foster a positive work environment that encourages ethical behavior at all levels.
The Essence of a Business Code of Ethics
Definition and Purpose
A Code of Ethics is a formal document or statement that outlines the ethical standards and expectations within an organization. It serves several critical purposes:
- Standard-Setting: It sets a clear benchmark for ethical behavior, helping employees understand what is expected of them.
- Guidance: It offers guidance on how to handle ethical dilemmas and make decisions that align with the organization’s core values.
- Accountability: It holds everyone in the organization accountable for their actions, promoting a culture of integrity.
- Reputation Management: It helps in building and maintaining a positive reputation, both internally and externally.
Components
The typical components of a code of ethics include:
- Core Values: These are the fundamental beliefs of the organization, such as honesty, integrity, and respect.
- Ethical Principles: These principles provide a framework for ethical decision-making. Examples include fairness, responsibility, and transparency.
- Behavioral Guidelines: Specific guidelines on expected behaviors in various situations. This may cover areas like conflicts of interest, confidentiality, and compliance with laws.
- Enforcement Procedures: Details on how the code will be enforced, including reporting mechanisms and potential consequences for violations.
- Support Resources: Information on resources available to employees for advice and guidance on ethical matters.
A well-crafted code of ethics not only outlines the ethical compass of an organization but also serves as a cornerstone for building a culture of integrity and ethical conduct.
Development and Implementation of a Code of Ethics in Business Ethics
Creating a Code of Ethics
The development of a code of ethics is a meticulous process that involves multiple steps:
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engaging different stakeholders, including employees, management, and possibly customers or suppliers, is crucial. Their input ensures that the code is comprehensive and reflective of the diverse perspectives within the organization.
- Alignment with Company Values: The code should be in harmony with the company’s mission and core values. This alignment ensures that the code is not just a document but a reflection of the organization’s ethos.
- Legal Considerations: Compliance with legal and regulatory standards is paramount. The code must adhere to all relevant laws and industry regulations to avoid legal pitfalls.
- Drafting and Review: Drafting the code is a collaborative effort, often involving legal counsel, HR, and ethics experts. Multiple reviews and revisions are typical to ensure clarity and completeness.
Implementing and Enforcing the Code
- Communication Strategies: Effective communication is key to the successful implementation of the code. This might involve presentations, written communications, and inclusive discussions to ensure that every employee understands the code.
- Training Programs: Regular training sessions help in reinforcing the principles and guidelines outlined in the code. These programs can be tailored to different levels within the organization and updated regularly to reflect any changes.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: A clear enforcement policy is essential. This includes establishing a reporting system for ethical violations, a process for investigating reports, and a transparent system of consequences for breaches of the code.
- Continuous Evaluation and Update: The code should not be static. Regular evaluations are necessary to ensure it remains relevant and effective, with updates made as needed in response to evolving business practices, legal requirements, and societal expectations.
The development and implementation of a code of ethics require thoughtful planning, active participation from various stakeholders, and a commitment to ongoing evaluation and reinforcement. This ensures that the code is not just a formal document, but a living framework guiding the organization’s ethical conduct.
Benefits of a Code of Ethics
Building Corporate Culture
A code of ethics plays a fundamental role in shaping and nurturing corporate culture:
- Alignment with Company Values: It serves as a tangible expression of the company’s core values and principles, guiding employee behavior to align with these values.
- Decision-Making Framework: By providing a clear framework for decision-making, it helps employees make choices that are not only legally compliant but also ethically sound.
- Promotes Ethical Awareness: Regular engagement with the code fosters a heightened awareness and understanding of ethical issues within the organization.
- Cultivates a Positive Work Environment: A well-implemented code can create a workplace atmosphere of integrity, respect, and ethical conduct, which contributes to employee satisfaction and retention.
Trust and Reputation
The impact of a code of ethics extends beyond the internal workings of a company, significantly influencing its external relations:
- Building Trust: Adherence to a code of ethics builds trust among customers, investors, and other stakeholders. It signals that the company is committed to doing business responsibly.
- Enhancing Reputation: A reputation for ethical conduct can be a powerful differentiator in the marketplace. It can attract customers, investors, and partners who value ethical practices.
- Mitigating Risks: A robust code of ethics can help mitigate risks by preventing unethical behaviors that could lead to legal issues or public relations crises.
- Long-term Success: Ethical practices contribute to the long-term success of a company. They foster loyalty among stakeholders and can lead to sustainable growth.
A code of ethics is not just a compliance tool, but a strategic asset that shapes corporate culture, builds trust, enhances reputation, and contributes to the long-term success and sustainability of an organization.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing a Code of Ethics in Business Ethics
Common Challenges
- Cultural Differences: In global organizations, diverse cultural norms can create conflicts in interpreting and applying the code of ethics.
- Compliance Issues: Ensuring that every employee, regardless of their role or level, complies with the code can be challenging.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to changes, especially if they perceive the code as restrictive or punitive.
- Enforcement Difficulties: Consistently enforcing the code across all levels of the organization can be difficult, particularly in larger, decentralized organizations.
- Keeping the Code Relevant: Ensuring the code stays up-to-date with evolving legal standards, industry practices, and societal expectations is a constant challenge.
Solutions and Best Practices
- Role of Leadership: Leaders should model the behavior they expect from their employees. By embodying the principles of the code, leaders can inspire others to follow.
- Continuous Training: Regular, engaging, and interactive training sessions help keep ethical standards at the forefront of employees’ minds. Tailoring training to specific roles or scenarios can make it more relevant and effective.
- Open Communication: Creating an environment where employees feel safe to discuss ethical dilemmas and report violations without fear of retribution is crucial. Regularly seeking feedback on the code and its implementation can also help.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Recognizing and respecting cultural differences while maintaining core ethical standards is important for global organizations. This might involve adapting certain aspects of the code to fit different cultural contexts, without compromising on key ethical principles.
- Regular Review and Update: The code should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the business environment, legal requirements, and societal values.
- Transparency in Enforcement: Establishing clear, fair, and consistent enforcement mechanisms ensures that the code is taken seriously and applied uniformly.
Overcoming the challenges in implementing a code of ethics requires a combination of strong leadership, ongoing education, open communication, cultural sensitivity, and a commitment to regular review and adaptation. These elements help create an ethical culture where the code of ethics is viewed as an integral part of daily business operations.
Case Studies
Case Studies: Implementing a Code of Ethics in Business Ethics
Case Study 1: Global Corporation Overcomes Cultural Barriers
Challenge: A multinational corporation faced difficulties in implementing its code of ethics across various countries due to cultural differences and varying legal standards.
Solution: The corporation tailored its training programs to address specific cultural contexts while maintaining core ethical principles. It also established a multilingual hotline for reporting ethical concerns, ensuring accessibility for employees in different regions.
Outcome: This approach led to a better understanding and acceptance of the code across the company’s global operations. The hotline saw increased usage, indicating a higher level of comfort in reporting ethical issues.
Case Study 2: Technology Company Tackles Resistance to Change
Challenge: A tech company encountered resistance from employees who viewed the new code of ethics as a hindrance to innovation and flexibility.
Solution: Leadership actively engaged with employees to communicate the importance of ethical conduct in sustaining long-term success. They used real-world examples to illustrate how ethical practices could coexist with innovation.
Outcome: Employees began to see the code as a framework for responsible innovation rather than a set of restrictions. This shift in perception helped integrate ethical considerations into the company’s innovative processes.
Case Study 3: Retail Giant Enhances Compliance and Enforcement
Challenge: A large retail chain struggled with ensuring compliance with its code of ethics, particularly in decentralized locations.
Solution: The company implemented a comprehensive compliance program, including regular audits and a clear, transparent process for handling violations. They also incentivized ethical behavior through recognition programs.
Outcome: The audit process and clear consequences for violations led to improved compliance. The recognition programs helped in promoting a positive view of the code, encouraging more employees to follow it.
Case Study 4: Financial Firm Updates Code to Stay Relevant
Challenge: A financial services firm found its code of ethics becoming outdated due to rapidly evolving industry regulations and societal expectations.
Solution: The firm established a routine for regularly reviewing and updating its code. They involved a diverse group of stakeholders in the review process to ensure that different perspectives were considered.
Outcome: The updated code remained relevant and effective in guiding employee behavior, and the firm maintained its reputation for high ethical standards.
Each of these case studies highlights the importance of addressing specific challenges in implementing a code of ethics and demonstrates how tailored solutions can lead to successful outcomes.
Examples of code of ethics in business ethics
Examples of Code of Ethics in Business Ethics
Example 1: Technology Company
Core Values: Innovation, Integrity, Respect for Individual Privacy
Principles:
- Encouraging creativity while ensuring ethical use of technology.
- Upholding honesty in all dealings.
- Respecting user data privacy and confidentiality.
Behavioural Guidelines:
- Prohibit misuse of user data.
- Mandate transparent communication in marketing.
- Establish a zero-tolerance policy for bribery and corruption.
Example 2: Retail Corporation
Core Values: Customer Satisfaction, Sustainability, Community Engagement
Principles:
- Prioritize customer needs and safety.
- Promote environmentally friendly practices.
- Engage in and support local communities.
Behavioural Guidelines:
- Ensure product safety and quality.
- Implement green practices in the supply chain.
- Encourage employee participation in community service.
Example 3: Financial Services Firm
Core Values: Trustworthiness, Accountability, Compliance
Principles:
- Maintain the highest level of integrity in financial dealings.
- Hold employees accountable for their actions.
- Adhere strictly to financial regulations and laws.
Behavioural Guidelines:
- Enforce strict confidentiality of client information.
- Require regular compliance training for employees.
- Implement rigorous auditing processes.
Example 4: Healthcare Provider
Core Values: Patient Welfare, Medical Ethics, Transparency
Principles:
- Prioritize patient health and safety.
- Uphold ethical standards in medical practices.
- Maintain transparency in patient care and billing.
Behavioural Guidelines:
- Ensure informed consent for treatments.
- Prohibit acceptance of gifts from pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandate clear communication of treatment costs and options.
Example 5: Manufacturing Company
Core Values: Quality, Safety, Fair Labor Practices
Principles:
- Commit to producing high-quality products.
- Ensure the safety of employees and consumers.
- Uphold fair labour practices in all operations.
Behavioural Guidelines:
- Regular safety training and audits.
- Maintain a workplace free from discrimination and harassment.
- Ensure fair wages and oppose child labour.
These examples showcase how businesses across various industries can design their codes of ethics to reflect their unique values and operational contexts, providing a framework for ethical decision-making and behaviour.
A Chart table for code of ethics in business ethics
I can provide a chart table summarizing key aspects of a code of ethics in business ethics. Here’s how it might look:
| Aspect | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Core Values | Fundamental beliefs that guide the organization’s behavior and decision-making. | Innovation, Integrity, Sustainability, etc. |
| Ethical Principles | Basic ethical standards the organization commits to uphold. | Honesty, Fairness, Respect, Responsibility. |
| Behavioural Guidelines | Specific rules and expectations for conduct, addressing various ethical scenarios the organization might face. | Conflict of interest policies, confidentiality rules, etc. |
| Enforcement Mechanisms | Procedures for ensuring compliance with the code, including reporting, investigation, and disciplinary actions for violations. | Ethics hotlines, disciplinary procedures. |
| Training Programs | Initiatives to educate employees about the code of ethics and ethical behavior in general. | Workshops, e-learning modules, seminars. |
| Review and Update | Regular assessment and revision of the code to keep it relevant and effective. | Annual reviews, updates in response to new laws or societal expectations. |
This table provides a structured overview of the components and considerations involved in a code of ethics within the context of business ethics.
An Infographic for code of ethics in business ethics Areas

Here is an infographic showcasing the key areas of a code of ethics in business ethics. This visual includes sections for Core Values, Ethical Principles, Behavioral Guidelines, Enforcement Mechanisms, Training Programs, and Review and Update, each with brief descriptions and symbolic icons or illustrations.
A graph for code of ethics in business ethics
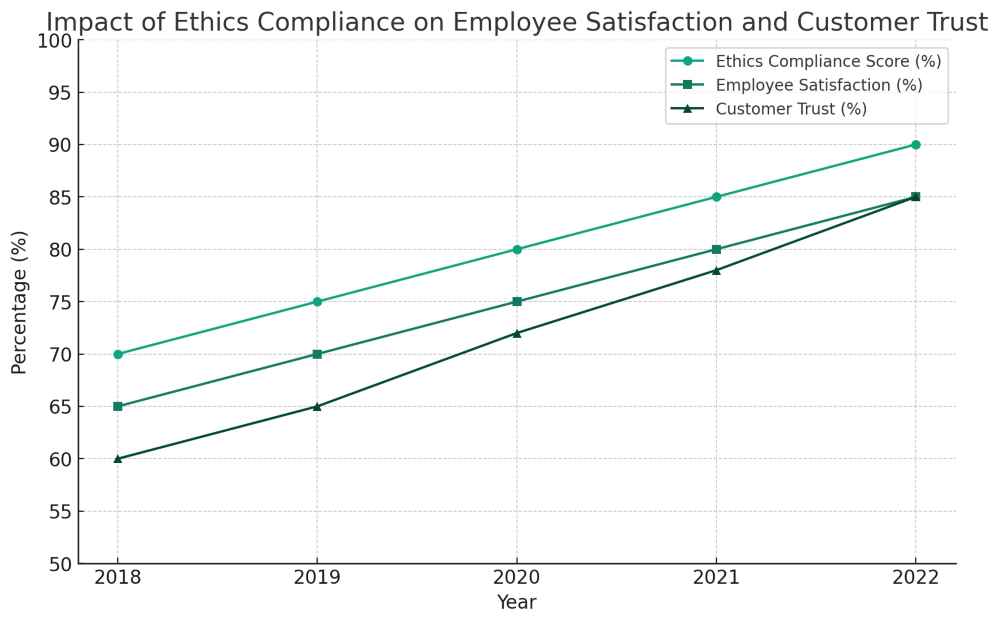
Here is a graph illustrating the hypothetical impact of ethics compliance on employee satisfaction and customer trust for years. The graph shows a positive correlation, indicating that as the ethics compliance score increases, there’s a corresponding increase in both employee satisfaction and customer trust percentages. This visualization helps in understanding how adhering to a code of ethics can positively influence key aspects of business performance.
Summary of Key Points
Definition and Importance: We began by defining business ethics and emphasizing the importance of a code of ethics in guiding business behavior and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
Essential Elements: We explored the essential elements of a code of ethics, including its definition, purpose, and typical components such as values, principles, and guidelines.
Development and Implementation: The process of creating and implementing a code of ethics involves stakeholder involvement, alignment with company values, legal considerations, effective communication strategies, training programs, and robust enforcement mechanisms.
Benefits: The benefits of a well-implemented code of ethics were highlighted, especially in building a positive corporate culture, enhancing trust and reputation among customers and investors, and contributing to the overall success of the business.
Challenges and Solutions: We addressed common challenges such as cultural differences, compliance issues, and resistance to change, and provided solutions like leadership involvement, continuous training, and open communication to overcome these hurdles.
Case Studies: Real-world case studies illustrated how different organizations have successfully navigated the complexities of implementing a code of ethics.
Graphical Representations: We used charts and graphs to visually represent the concepts and data related to the code of ethics in business ethics.
Call to Action
In today’s dynamic and often challenging business environment, the adoption and rigorous enforcement of a code of ethics is more than just a legal or regulatory necessity; it’s a cornerstone for building a sustainable and respected business. A well-crafted and diligently implemented code of ethics serves as a guiding light for organizational behavior, fostering a culture of integrity and ethical decision-making that resonates with employees, customers, and the broader community.
I encourage all businesses, regardless of size or industry, to embrace the development and enforcement of a comprehensive code of ethics. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about setting a foundation for long-term success, building trust, and maintaining a positive reputation in an increasingly complex and interconnected world. Let your code of ethics be a clear statement of your commitment to ethical business practices, reflecting who you are as an organization and how you aspire to operate every day.

Conclusion
As we conclude, it’s clear that the role of a code of ethics in business cannot be overstated. It’s not just a set of rules; it’s a reflection of a company’s identity and values. This code serves as a compass guiding employees through ethical dilemmas and fostering a culture of integrity and responsibility.
The benefits of having a robust code of ethics are manifold. It shapes corporate culture, aligns employee behavior with organizational values, builds trust with stakeholders, and enhances a company’s reputation. These factors collectively contribute to the sustainable success of the business.
However, developing and implementing a code of ethics is not without its challenges. Companies often grapple with cultural differences, compliance complexities, and resistance to change. Overcoming these hurdles requires a strategic approach involving inclusive stakeholder engagement, alignment with core values, and ongoing training and communication.
Real-world case studies have illustrated the tangible impact of effectively implemented ethical codes, highlighting improved trust, culture, and business performance. Graphical representations further underscore how adherence to ethical principles positively correlates with various business metrics.
The significance of a code of ethics in today’s business landscape is profound. Businesses are encouraged to not only adopt but rigorously enforce a code of ethics. Doing so is fundamental not just for legal and regulatory compliance, but for nurturing an environment of ethical behavior that supports long-term growth and success. An effective code of ethics is not just good practice; it’s a strategic asset in building a trustworthy and enduring business.
References
For information about the code of ethics in business ethics, you can refer to a variety of reliable sources. These include:
Academic Journals: Journals such as the “Journal of Business Ethics” often publish articles on this topic. You can access these through academic databases like JSTOR or Google Scholar.
Professional Organizations: Websites of professional organizations like the Ethics & Compliance Initiative (ECI) at https://www.ethics.org often have resources and best practices on corporate ethics.
Business Websites: Many corporations publish their codes of ethics online. These can be found on their official websites in sections typically labelled as ‘Corporate Governance’ or ‘Ethics and Compliance’.
Government Resources: Government agencies, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), provide guidelines and regulations relevant to business ethics. Visit https://www.sec.gov for more information.
Educational Websites: Universities and business schools often provide resources and case studies on business ethics. Websites like Harvard Business Review (https://hbr.org) are also valuable resources.
These sources can offer a comprehensive understanding of the code of ethics in business ethics, including its development, importance, and practical applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the code of ethics in business ethics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Code of Ethics in Business Ethics
- What is a Code of Ethics in Business?
A Code of Ethics is a formal document that defines the ethical standards and guidelines for behavior within an organization. It outlines the company’s values, principles, and expectations for ethical conduct.
- Why is a Code of Ethics Important in Business?
It guides decision-making, aligns behavior with the organization’s core values, fosters a positive corporate culture, builds trust with stakeholders, and protects the company’s reputation.
- Who is Responsible for Developing a Code of Ethics?
Typically, the development of a code of ethics is a collaborative effort involving senior leadership, human resources, legal counsel, and often input from employees and other stakeholders.
- How is a Code of Ethics Different from a Code of Conduct?
A code of ethics is about values and principles guiding behavior, while a code of conduct provides specific guidelines for actions and behaviors in various scenarios.
- How Should a Code of Ethics be Implemented?
Implementation should include clear communication, regular training, integration into corporate culture, and a system for enforcement and reporting.
- What Happens if Someone Violates the Code of Ethics?
Violations typically lead to disciplinary actions, which can range from warnings to termination, depending on the severity of the breach.
- Is a Code of Ethics Legally Binding?
While not a legal document, a code of ethics can have legal implications. It often aligns with legal standards and can be used in legal proceedings to demonstrate company policy.
- Can a Code of Ethics Change Over Time?
Yes, it should be reviewed regularly and updated as needed to reflect changes in the company, industry standards, and societal expectations.
- How Do Cultural Differences Affect a Code of Ethics?
Global companies need to consider cultural differences in ethical perceptions and practices and may need to adapt their code accordingly while maintaining core ethical standards.
- How Can Companies Ensure Compliance with the Code of Ethics?
Through regular training, clear communication, effective enforcement mechanisms, and fostering an ethical corporate culture.
These FAQs cover the basic aspects of a code of ethics in business ethics, offering insights into its development, importance, implementation, and maintenance within an organization.









Leave a Reply